Feature Overview
IoT Hub (TB) Entity Views (EVs) are available since v2.2. This feature was requested by many TB users. Similar to SQL database views, which limits the degree of exposure of the underlying tables to the outer world, TB EVs limit the degree of exposure of the Device or Asset telemetry and attributes to the Customers. As a Tenant Administrator, you are able to create multiple EVs per Device or Asset and assign them to different Customers.
Supported use cases:
- Share specific device or asset data with multiple Customers simultaneously. Prior EVs feature was not possible due to restrictions of the TB security model.
- Allow particular Customer users to see collected data (e.g. sensor readings), but hide debug info like battery level, system errors, etc.
- Device-as-a-Service (DaaS) model where data collected by the device at different periods of time belongs to different Customers.
Architecture
Entity View contains the following information:
- TenantId - represents a link to the owner of the view;
- CustomerId - represents a link to the customer that has access to the view;
- EntityId - represents a link to the target device or asset;
- Name and type - regular IoT Hub entity fields that are used for display and search purposes;
- Start and end time - represents the time interval that is used to limit access to target device telemetry. Customer will not be able to see entity telemetry that is outside the specified interval;
- Time series keys - list of time series data keys that are accessible to the viewer;
- Attribute keys - list of attribute names that are accessible to the viewer;
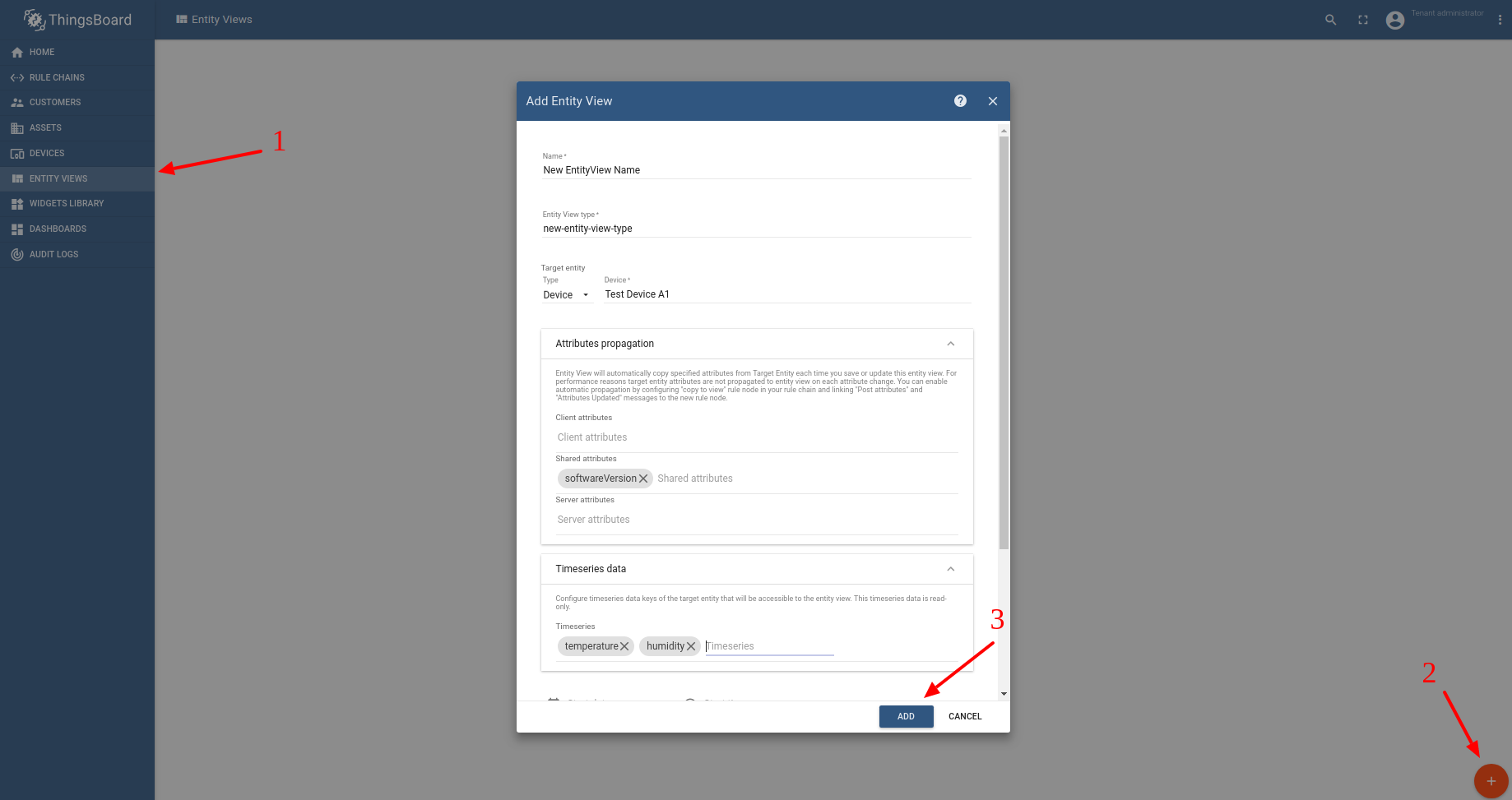
It is important to understand how TB handles telemetry and attribute updates, and how these changes affect Entity Views.
Time series data view
All time series data is stored in the database on behalf of the target entity. There is no time series data duplication to any of the Entity Views. When a user opens a dashboard or performs a REST API call on behalf of the entity view ID, the following actions take place:
- Request start and end timestamps are validated and adjusted to fit into Entity View start and end time. Thus, if Dashboard tries to fetch 1 year of data, but EV is configured to access only 6 months of data, it will fail to do so.
- Request time series data keys are validated and adjusted based on time series data keys provisioned in the Entity View. Thus, if Dashboard tries to fetch the telemetry keys that are forbidden for this particular view, it will fail to do so.
Attributes view
Entity View automatically copies specified attributes from Target Entity each time you save or update this entity view. For performance reasons, target entity attributes are not propagated to entity view on each attribute change. You can enable automatic propagation by configuring a “copy to view” rule node in your rule chain and linking “Post attributes” and “Attributes Updated” messages to the new rule node.
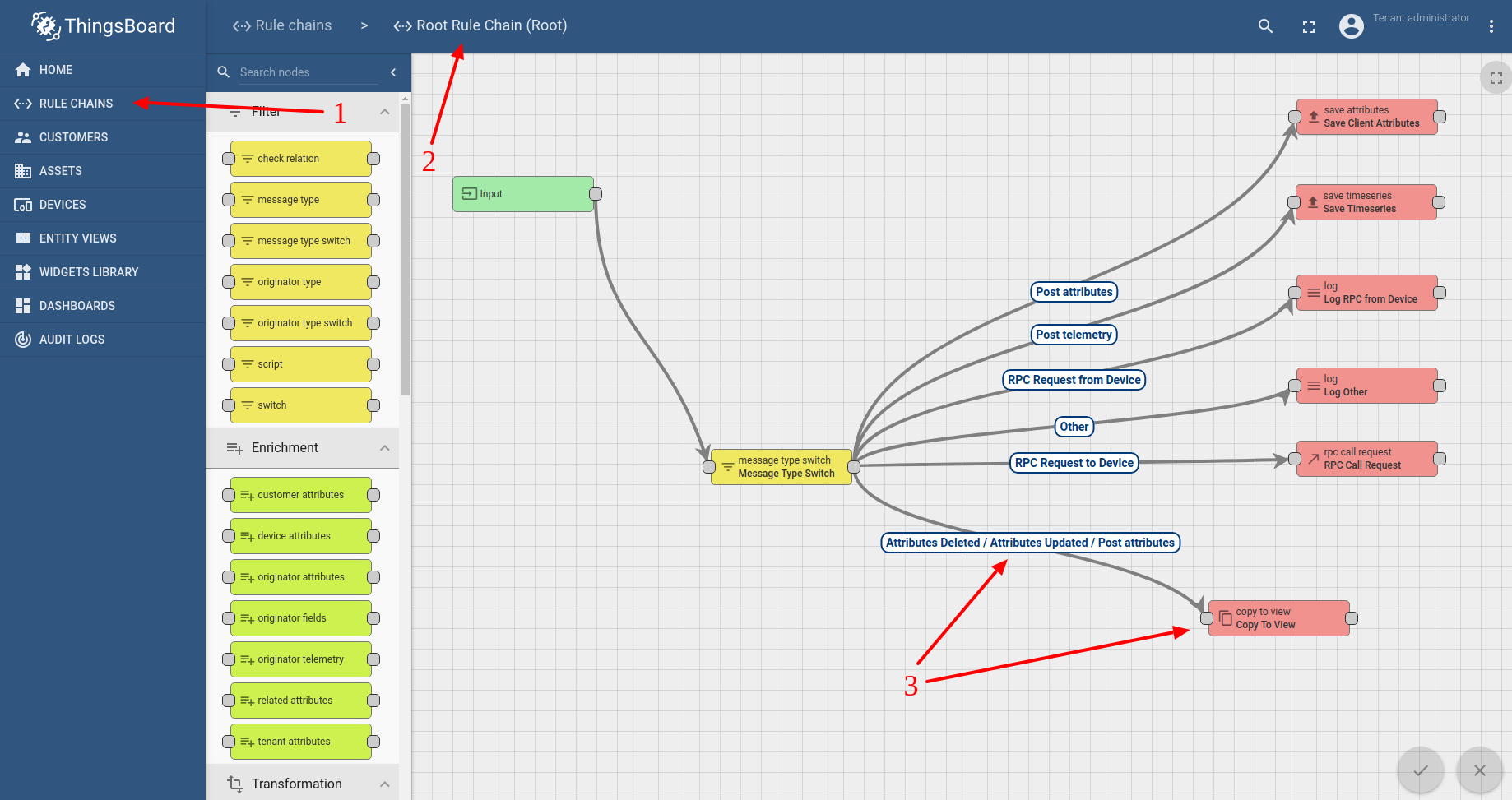
Future improvements
There are the following features in IoT Hub Road Map:
- Add the ability to enable/disable RPC requests to the device view;
- Add the ability to configure a list of alarms that are accessible(propagated) for a particular view.
Next steps
- Getting started guides - These guides provide quick overview of main IoT Hub features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes.
-
Connect your device - Learn how to connect devices based on your connectivity technology or solution.
-
Data visualization - These guides contain instructions how to configure complex IoT Hub dashboards.
-
Data processing & actions - Learn how to use IoT Hub Rule Engine.
-
IoT Data analytics - Learn how to use rule engine to perform basic analytics tasks.
-
Hardware samples - Learn how to connect various hardware platforms to IoT Hub.
-
Contribution and Development - Learn about contribution and development in IoT Hub.